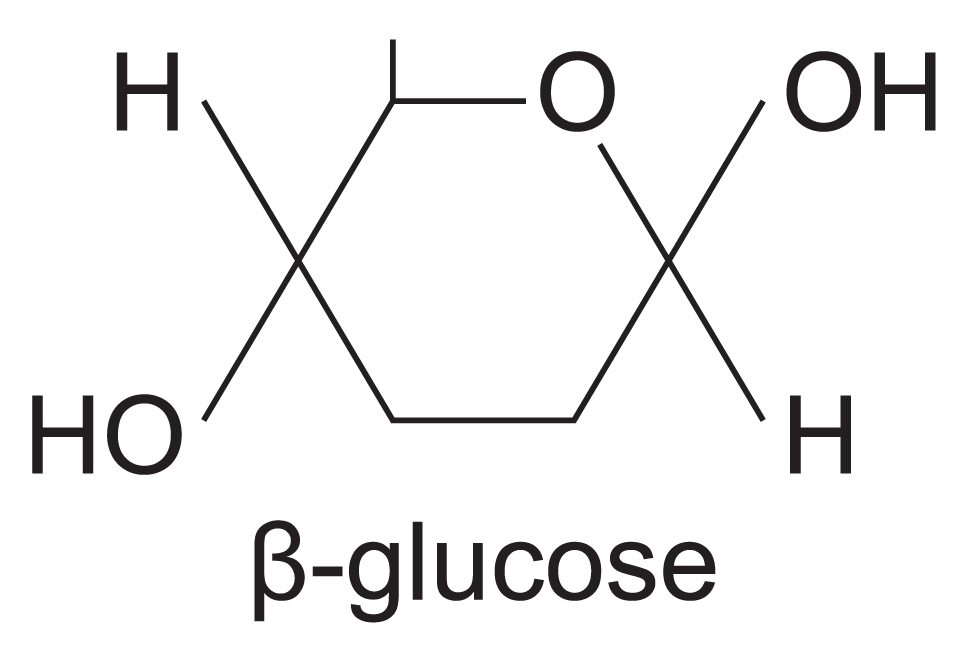3.1.2 Carbohydrates
Content |
Opportunities for skills development |
|---|---|
|
Monosaccharides are the monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made. Glucose, galactose and fructose are common monosaccharides. A condensation reaction between two monosaccharides forms a glycosidic bond. Disaccharides are formed by the condensation of two monosaccharides:
Glucose has two isomers, α-glucose and β-glucose, with structures:
Polysaccharides are formed by the condensation of many glucose units.
The basic structure and functions of glycogen, starch and cellulose. The relationship of structure to function of these substances in animal cells and plant cells. Biochemical tests using Benedict's solution for reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars and iodine/potassium iodide for starch. |
AT f Students could use, and interpret the results of, qualitative tests for reducing sugars, non-reducing sugars and starch.AT g Students could use chromatography, with known standard solutions, to separate a mixture of monosaccharides and identify their components. AT c Students could produce a dilution series of glucose solution and use colorimetric techniques to produce a calibration curve with which to identify the concentration of glucose in an unknown solution. |