Specifications that use this resource:
Teaching guide: income elasticity demand
This measures the sensitivity of demand to changes in income.
Equation
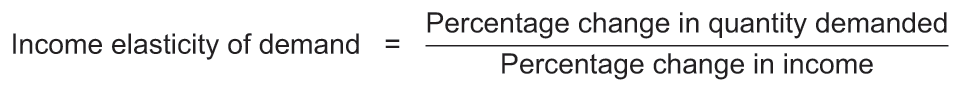
Key points
A positive answer means that an increase in income increases quantity demanded (and vice versa). For example, with more income households may take more foreign holidays.
A negative answer means that an increase in income decreases quantity demanded (and vice versa). For example, with more income households may spend less on UK holidays as they go abroad more. If demand for a product falls as income increases this is known as an 'inferior' product.
The value of the answer (ie the size of the answer ignoring the sign) shows how sensitive demand is to changes in income. The bigger the number the more responsive demand is.
- If the income elasticity is 2 this means a 1% change in income leads to a 2% change in quantity demanded.
- If the income elasticity of demand is 0.5 this means a 1% change in income leads to a 0.5% change in quantity demanded.
- If the value of the income elasticity of demand is greater than 1 this is known as income elastic demand. If the value of the income elasticity of demand is less than 1 this is known as an income inelastic demand.
When you can use this
- when studying influences on demand
- when studying correlation (it shows how one variable changes when another one changes)
- when considering how a business might prepare for or be affected by changes in the incomes of its customers (ie, changes in revenue may be affected by demand and this in turn will influence factors such as cash flow, profit forecasts, inventory and human resource planning).
Where it's been used
-
Q20, A-level paper 1, 2017
-
Q3, AS paper 1, 2018
-
Q9, AS paper 1, SAM set 1