Specifications that use this resource:
Teaching guide: Bartlett and Ghoshal's international, multi-domestic, transnational and global strategies (for last exams in 2024)
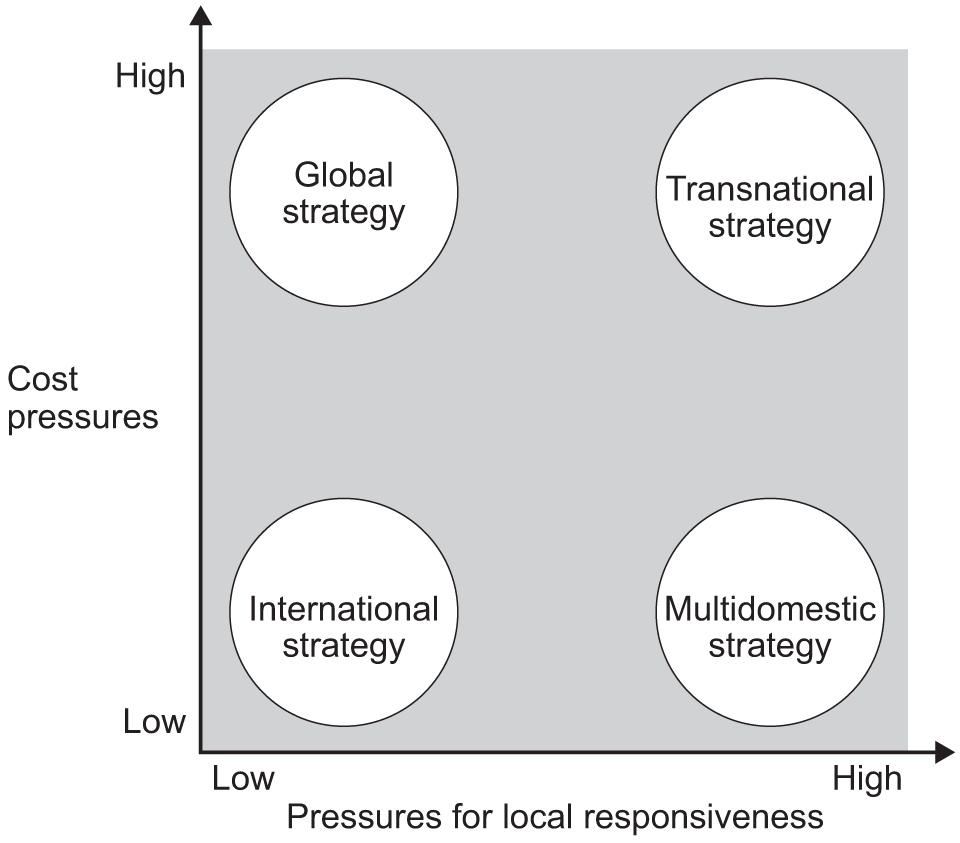
This model examines the different approaches to managing businesses that operate in several countries. It highlights two key factors in choosing how to manage an international business: the potential cost gains from being globally integrated (such as marketing, production or research economies of scale) and the pressures to respond to local market conditions.
Model/theory
Key points
The strategy adopted by a business will depend on the relative strength of market forces.
International strategy
An international strategy occurs when there are similarities between markets and little gains from globally integrating. The result is a business operating abroad but run very much from the home country. The head office and main decisions will be based at home.
Multi-domestic strategy
A multi-domestic strategy occurs when there are considerable variations between market demands and few benefits from globally integrating. The result will be a portfolio of relatively independent companies running themselves and producing for their own markets.
Global strategy
A global strategy occurs when there are significant economies of scale and where there are similarities in terms of market demand. The business develops standardised products which are sold globally. The subsidiaries abroad are likely to be rather weak and the full range of business activities will only exist in the home market. The products are designed and developed in the domestic country.
Transnational strategy
A transnational strategy occurs when there is pressure to meet local needs and also benefits from integrating globally. The organisation is regarded as a network with each subsidiary given responsibility appropriate to its capabilities. There is a balance of centralisation and decentralisation and a culture of sharing within the global organisation. Staff move around the business globally which helps build shared values and shared knowledge.
When you can use this
When discussing international business and the best strategy to adopt when operating overseas.
- It highlights that conditions in terms of cost saving and market differences will vary and that this will influence the management strategy adopted.
- It highlights that multinational companies can be managed in very different ways: for example, power may be kept very much within the home country or may be diffused throughout the world; products may be standardised or varied according to different market needs.
Where it's been used
Q4, A-level paper 1, SAM set 2