Specifications that use this resource:
Teaching guide: Bowman's strategic clock (for last exams in 2024)
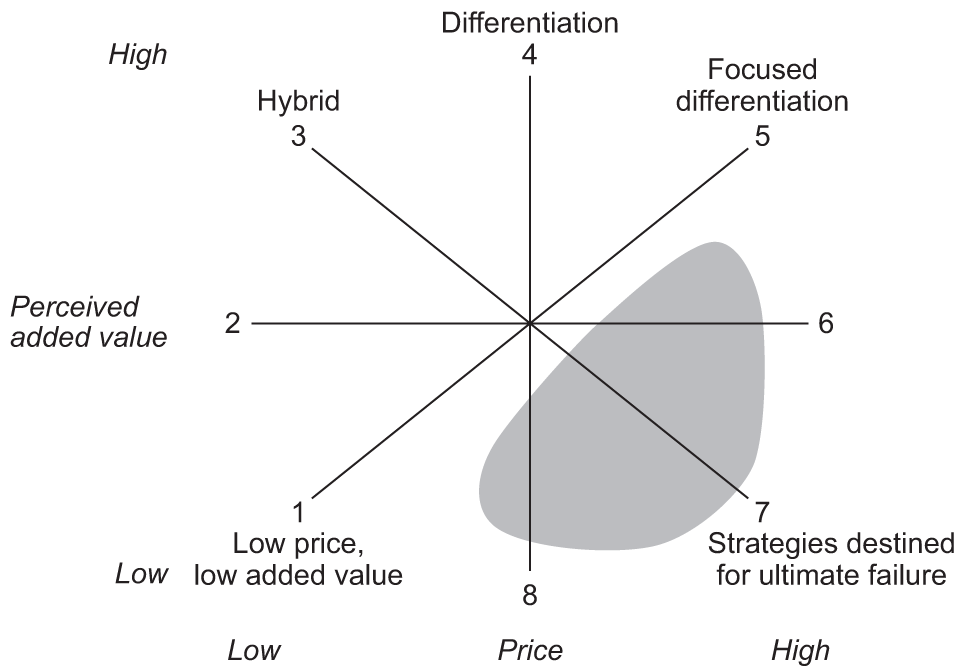
This outlines different strategies in terms of the perceived benefits (added value) and price. It highlights different combinations of benefits and price that are competitive and those that are not.
Model/theory
Key points
This model shows that:
- Different strategies can be competitive: for example, a business can charge a high price if it offers a high level of benefits and be competitive. If it offers relatively low benefits it needs a low price to compete.
- Some combinations of benefits and price are not competitive, eg low benefits and high price is unlikely to be competitive. These are shown by the shaded area.
When you can use this
When teaching strategy:
- you can plot different strategies adopted by organisations and assess their competitiveness
- you can plot how businesses may be trying to change their strategy (eg some mainstream supermarkets trying to reduce prices to match the discounters)
- you can consider why some strategies are unsuccessful
- you can link with Porter’s low cost and differentiation strategies
- you can consider how businesses will try to increase their competitiveness, eg by offering more benefits at the same price or the same benefits at a lower price.
Where it's been used
Q12, A-level paper 1, SAM set 1